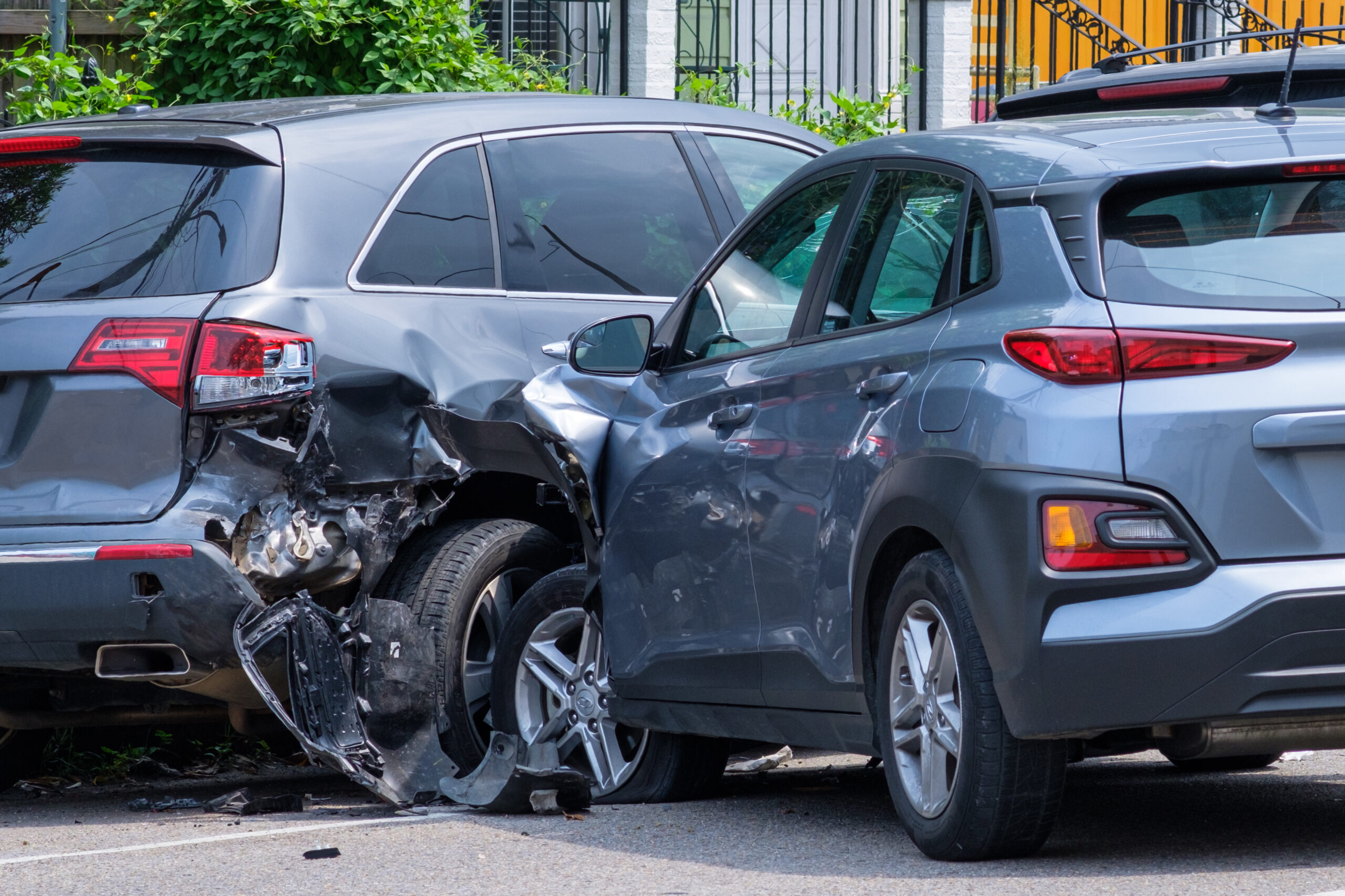
Being in a car accident can be traumatic. In the immediate aftermath of the crash, your body protects itself by releasing a rush of adrenaline to dull the physical and emotional shock of the event. But, unfortunately, this can also hide the severity of any underlying injuries — with potentially severe consequences.
Delayed pain is a significant issue. Insurers may try to deny your claim or refuse to pay you fair compensation for your injuries. They may even claim your delayed pain was not caused by the crash. The personal injury lawyers at Stokes Stemle, LLC have seen this tactic used against car accident victims before and know how to fight back.
You could be owed compensation if you’ve suffered delayed pain after a car wreck that led to painful complications. Get in touch with the Alabama car accident attorneys of Stokes Stemle, LLC, to find out how we can help you pursue it. Our team is focused on providing excellent legal advice and effective representation. And because we don’t charge any upfront fees, there’s no risk in demanding the justice you deserve.
What Causes Delayed Pain After an Auto Accident?
Car accidents can cause many types of injuries. Some might be obvious, such as severely broken bones or burns. Other injuries are more subtle and can take time to manifest themselves. For example, concussions, whiplash, and back problems may not be immediately apparent in the initial aftermath of an accident.
That’s because delayed pain after a car crash is quite common. Our bodies are excellent at hiding pain in stressful situations so we can function long enough to survive the initial trauma. Sometimes, it can be days or weeks before the body begins to register something wrong.
The Fight or Flight Response
There are sound medical reasons why some injuries present with delayed pain and symptoms. The first is the massive rush of adrenaline that floods your system moments after a severe accident. Adrenaline is a chemical that helps your body respond to traumatic or dangerous situations. It’s what keeps you alive and triggers your fight-or-flight response.
Adrenaline works by effectively shutting down non-essential systems of the body. As a result, adrenaline can make you feel stronger and more alert. It can also limit pain signals transmitted to the brain. Essentially, it hides the ability to feel pain in certain situations.
You may be hurt after a car wreck, but the adrenaline surge in your body can mask the pain that would otherwise alert you to the injury. It can take hours or even days for your hormonal levels to balance out after a traumatic event. As a result, you may not notice the pain until your adrenaline levels normalize.
You Could Be in Shock
You may be in shock after a devastating car crash —not just emotional but physical shock. Shock is a medical condition triggered by intense trauma. It is a critical response to a sudden drop in blood flow. Shock can be caused by blood loss, infection, severe burns, or an allergic reaction.
When shock sets in, the body’s internal organs don’t get enough blood or oxygen to function. The body may try to overcompensate and redirect blood to the organs. Victims experiencing shock may have cool or clammy skin, muscle weakness, blue fingertips or lips, and tingling or a loss of sensation in their extremities.
If treated quickly, shock may only last for a short time. However, going through shock may mask the signs of other injuries for a few hours to a few days.
How Long After a Car Accident Can Symptoms Appear?
Not everyone responds to trauma in the same way. Different people may experience the symptoms of their injuries differently over different time frames. Generally, delayed pain after a car accident can begin to present itself hours or days after the initial impact. In some cases, it may take a week or more before someone who’s been in an accident is fully aware of their injuries.
Some of the most common symptoms of delayed car accident injuries include the following:
- Headache
- Confusion
- Pain
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Numbness or tingling
- Intense bruising
- Behavioral changes
Some of the injuries that most commonly take time to manifest themselves include the following:
- Concussions– Concussions are common after serious car crashes. Unfortunately, it can take hours or days for a person to realize that they have been concussed. Adrenaline is particularly good at masking the signs of a concussion. Talk to your doctor immediately if you experience headaches, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, confusion, abnormal sleep patterns, or mood problems.
- Whiplash – It can take time for the muscles in our bodies to fully register trauma, such as with whiplash. You may feel pain in your neck immediately after a crash that fades as your adrenaline kicks in. It can take days for the muscles to register that they are injured and send pain signals back to the brain.
- Internal bleeding – Internal bleeding is not often considered a delayed injury. However, small internal bleeds can sometimes take days to cause significant symptoms. As the bleeding continues, symptoms will get progressively worse. If not treated, internal bleeding can result in death. Signs of internal bleeding include abdominal pain or swelling, dizziness, and large or deep purple bruise-like marks on the skin.
- Spinal cord injuries – While some spinal injuries are immediately apparent; others are not. For example, herniated discs don’t necessarily hurt right away and may take time to bulge to the point where they can cause pain and loss of sensation. A traumatic car accident can also chip a vertebra in the spine. It’s not until you move a certain way that the bone chip slices into the spinal cord, causing pain, loss of sensation, numbness, or even paralysis.
- Soft tissue injuries– Injuries impacting the muscles and soft tissues of the body can take time to fully manifest. Sprains and strains are often overlooked, especially when there are more immediately obvious or severe injuries. However, they can cause significant problems and should be addressed as soon as possible. If you notice pain, swelling, tenderness, or a loss of range of motion, talk to your doctor.
You should always see a doctor as soon as possible after a car accident. You may have suffered injuries you don’t know about yet. Even if you have already seen a doctor, talk to your physician again and seek appropriate treatment options if you notice new or worsening symptoms.
Not seeking medical attention quickly can jeopardize your safety and ability to recover the compensation you deserve. Many insurers will deny a claim if there is no medical documentation supporting your injury status.